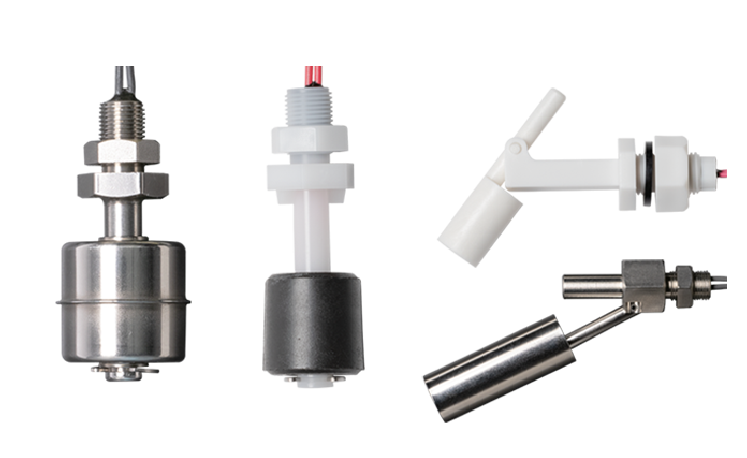
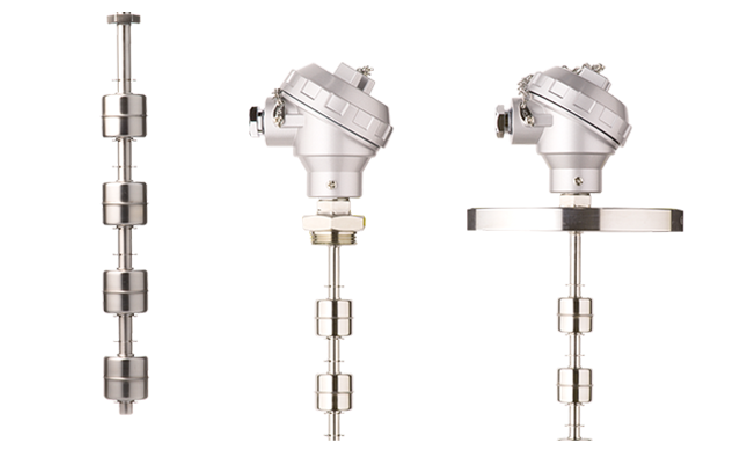
Basics of Float-Type Level Switches

This type of sensor, which precisely detects and measures the amount of liquid inside a container or the like, is generally referred to in short as a “float switch.”As a usage example, when the liquid level in the container rises and the liquid level exceeds the standard (or vice versa), it causes the level switch to contact (detection), triggering a beep sound and activating a control unit. In other words, it has an important control function.
Riko’s float-type level switch flexibly accommodates
the movement of specific liquids.
As liquid flows, the float rises and falls, enabling the float-type level switch to detect the liquid level (as a liquid surface) as the reed switch inside the main unit cycles between ON and OFF status from the magnetic force of the magnet contained in the float.
General Applications
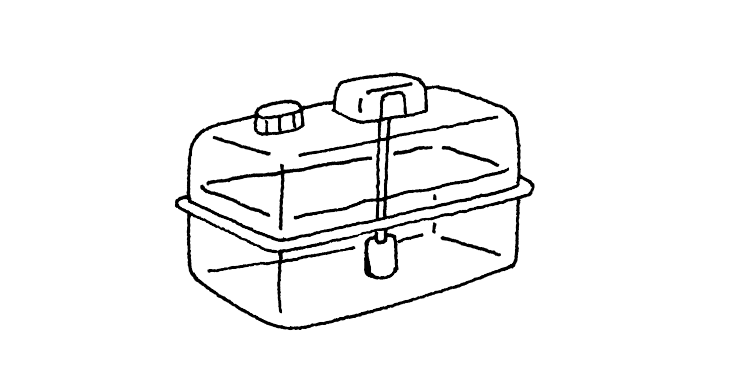
Detection of a liquid quantity
and control of an electric system
Generally, an alarm triggers a lamp or buzzer from the electrical signal generated when the float switch detects that the liquid in a tank is depleted or replenished. This approach is used in many control systems that actuate or turn off a motor or heater by closing or opening a power supply
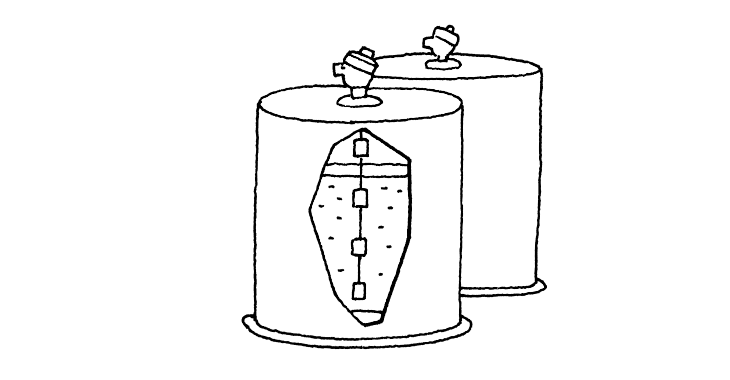
Widely used in liquid level control
The float-type level switches are available with one, two or three contact points, allowing you to select the most suitable for a particular application. All models are used for control of a liquid level and can be used in various industrial plants, unmanned flexible manufacturing systems, space heating and cooling units, washing devices, and various medical applications for the health-care profession.
Typical applications of the float-type level switches
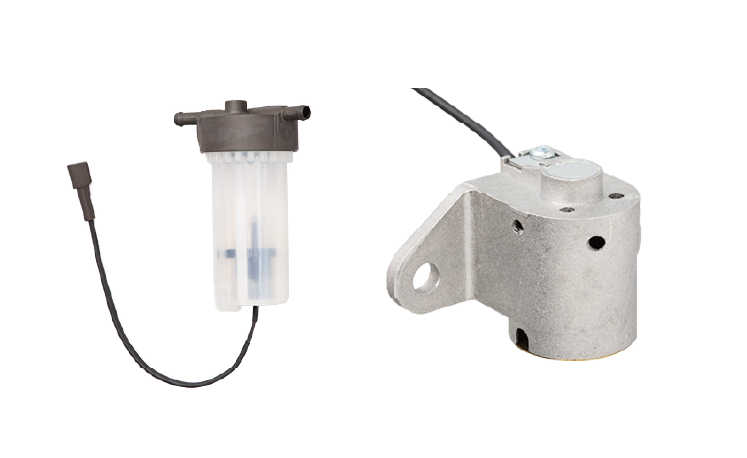
Kerosene heaters
Shuts off the combustion pump and triggers a lamp and buzzer when the kerosene is depleted.
Motor vehicles
Illuminates a warning lamp on the instrument panel when the brake fluid runs low.
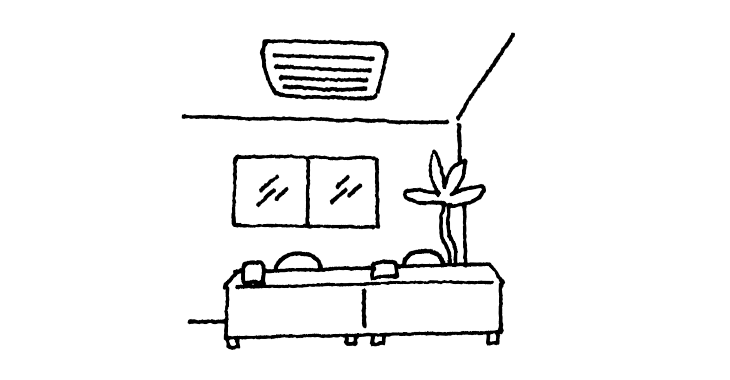
Commercial-duty air conditioners
Turns on a pump to drain the water when the drain pan of a ceiling-recessed air conditioner is full.
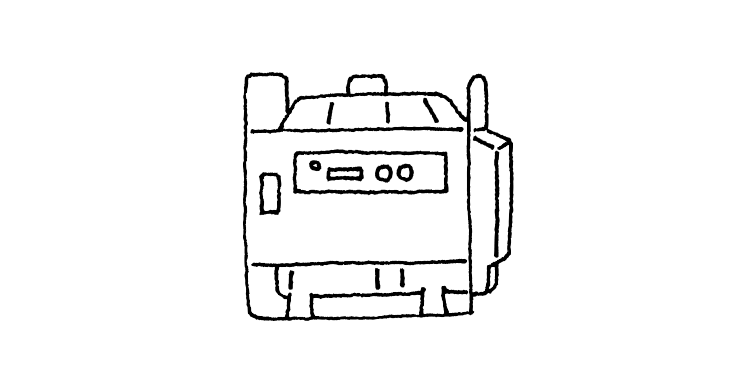
General-purpose engine
Lights a lamp and shuts down the engine when the oil level is low in a general-purpose engine used for the generator of a food stall or outdoor facility.
Other applications
- Heated toilet seats
- Car wash machinery
- Diesel equipment
- Buses
- Marine vessels
- Agricultural machinery
- Machine tool lubricant
- Fast photo developing machines
- Trucks
- Locomotives
- Construction machinery
Structure & Operation principle
of the reed switch
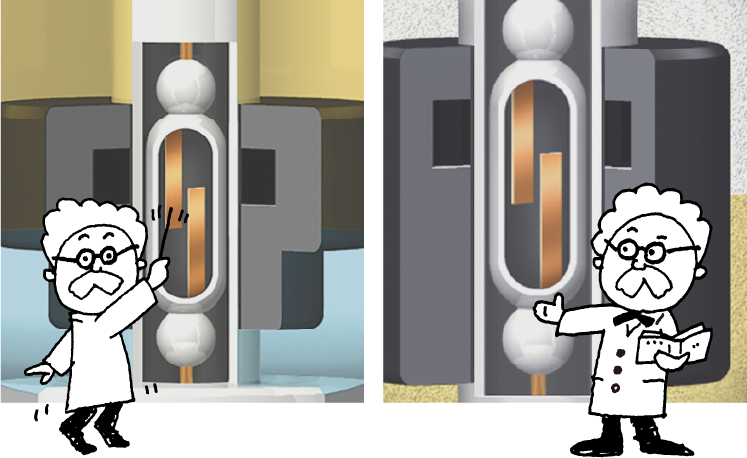
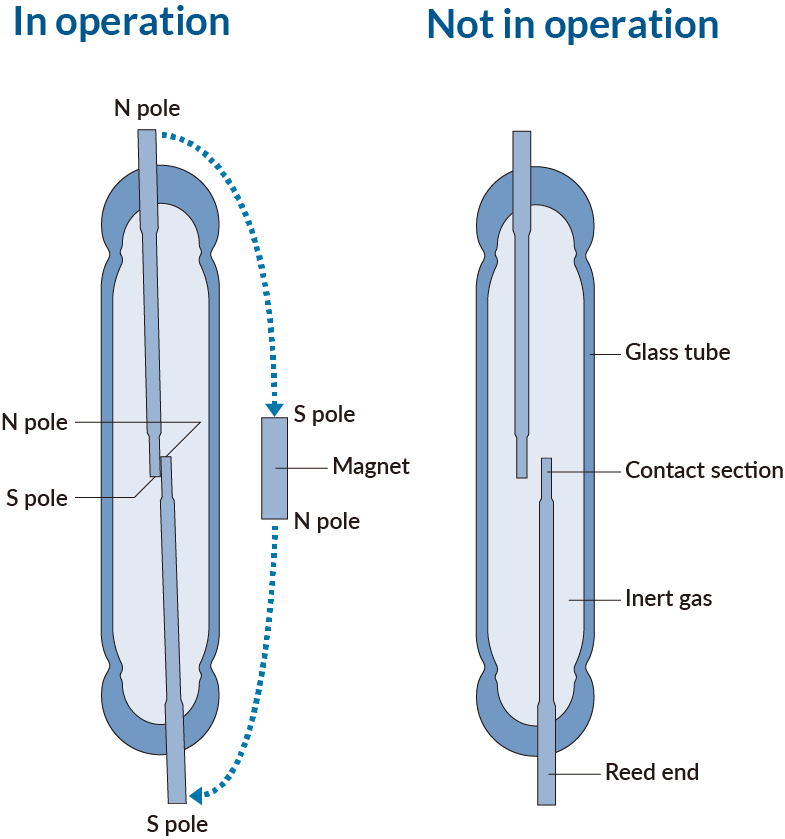
A reed switch is mounted inside the stem of the float. The magnetic field of the N pole and S pole generated by the magnet acts on the reed section of the float, which enters the ON state as a result of magnetic attraction. When the magnet is moved away, the magnetic field is removed and the reeds’ elasticity opens the contacts, restoring the OFF state.
As shown in the figure, a reed switch comprises two ferromagnetic reeds enclosed within a glass tube. To prevent oxidation (rust) of the points of contact, the tube is filled with an inert gas (nitrogen) and the surfaces of the points of contact are plated with a noble metal such as rhodium. (In the case of a single reed switch, the contacts are spread apart.)
Model nomenclature

Base material of product
(such as stem and float) is plastic.

Base material of product
(such as stem and float) is stainless steel.
Examples of model names
| MFS17-A | MFS (base material: plastic), 17 (model, development no.), A (float number). The MFS series includes a float number because in many cases only the float material differs from that of the stem of the same model. In some cases, different materials can have the same shape. |
|---|---|
| RFS-2 | RFS (base material: stainless steel), 2 (model, development no.) With the RFS series, a model without a stainless steel float is indicated as RFS-2; a model provided with a “B float” is indicated as RFS-2B. |
| PVC-2C | Essentially the same as the RFS Series but designed with PVC (polyvinyl chloride) as the base material. |
| RFS-12H | The meaning of the “H” suffix in models RFS-11H and RFS-12H is not the same as the “H” prefix in HFS-2, which indicates a heat-shock-resistant type. |

Explore the “Basics of Level Switches” on the following sites by RIKO Float Technology CO., LTD. (RFT):